Pancreas Transplant
Pancreas transplant and failure
Non-surgical pancreas failure treatment
Innovative approaches to managing pancreatic disorders without surgery encompass medications, dietary management, and targeted therapies that focus on the specific needs of the pancreas. These non-invasive methods address conditions like pancreatitis, pancreatic insufficiency, and diabetes, providing patients with effective alternatives to surgical intervention in the early stages of the disease.
One of the main functions of the pancreas is to make insulin, a hormone that regulates the absorption of sugar into cells. If the pancreas doesn't make enough insulin, blood sugar levels can rise to unhealthy levels, resulting in type 1 diabetes. Non-surgical treatments enable more accurate diagnostics and personalized treatment plans like:
- Innovative techniques such as high-resolution MRI and advanced ultrasound methods provide detailed insights into pancreatic structures, facilitating early detection and better management of disorders.
- Wearable devices and mobile health applications that monitor their glucose levels, dietary intake, and overall health metrics in real time.
- Medications that target enzyme deficiency, inflammation, and insulin resistance such as pancreatic enzyme replacements and medications that improve insulin sensitivity.
- Diet and lifestyle changes that include avoiding high-fat, high-sugar foods can significantly reduce the strain on the pancreas, promoting better digestion and reducing inflammation. Regular physical activity, stress management, and avoiding alcohol and tobacco are also key.
Pancreas surgery and transplant
Pancreas tumor surgery
A minimally invasive Hepatobiliary surgery involves removing benign and malignant tumors of the liver or pancreas but leaves surrounding tissue. It utilizes smaller incisions that help decrease pain, length of hospital stays, and recovery time. Our surgeons use laparoscopic techniques whenever possible to inspect the abdomen, remove, and destroy tumors.
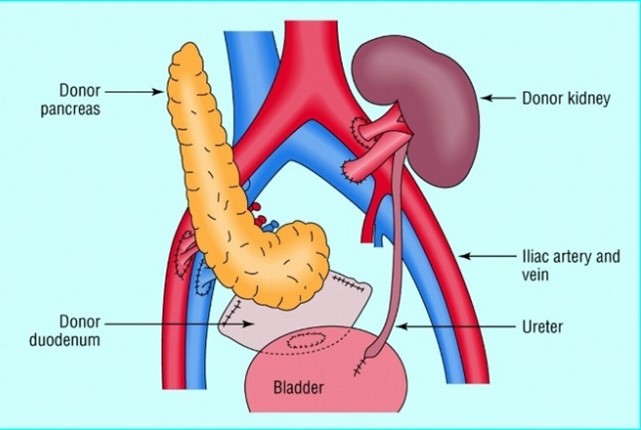
Pancreas transplant
A pancreas transplant is typically reserved for those with serious complications of diabetes because the side effects of a pancreas transplant can be significant. The most common reason for a pancreas transplant is to restore insulin production in people with type 1 diabetes, reducing or eliminating the need for insulin therapy. It’s considered when complications from diabetes pose a significant risk for those with:
- Type 1 diabetes that cannot be controlled with standard treatment
- Frequent insulin reactions
- Consistently poor blood sugar control
- Severe kidney damage
- Type 2 diabetes associated with both low insulin resistance and low insulin production
Pancreas transplantation involves surgically replacing the diseased liver with a new one to restore normal function requiring lifelong medication management to prevent rejection.
Learn more about pancreas transplants
Questions?
To learn more, please contact the Tulane Transplant Institute at 504-988-5344.

